Template Method Pattern In Java
Introduction:
The template method pattern is a behavioral pattern which suggests defining an algorithm more generally in the superclass. The algorithm is defined within a method known as the template method. The subclasses only define the implementation of the more specific algorithmic steps.
The benefit of using this design pattern is that any changes later in the algorithm will only impact the code in the superclass. Also, it promotes code reusability.
In this quick tutorial, we’ll learn to implement the template method pattern in Java.
Template Method Pattern:
Let’s say we have to write an essay. There are generally a few steps involved:
- research on the topic
- make an outline
- write the introduction
- Then, prepare the body of the essay
- finally, end it up with the conclusion
So, let’s go ahead and create an EssayTemplate class:
public abstract class EssayTemplate {
private String topic;
public EssayTemplate(String topic) {
this.topic = topic;
}
public final void writeEssay() {
doResearch();
makeOutline();
writeIntro();
writeBody();
writeConclusion();
}
void doResearch() { System.out.println("Researching"); }
void makeOutline() { System.out.println("Making an outline"); }
void writeIntro() { System.out.println("Introducing topic"); }
void writeConclusion() { System.out.println("Concluding topic");}
abstract writeBody();
}
Most of the general steps including researching, creating an outline, writing an introduction and the conclusion will remain the same, irrespective of the type of essay – short or long. So, these method definitions are present in the superclass itself.
Also, note that we have marked our template method to be final to avoid it being overridden by any of the subclasses.
Using the Template Class:
The main content or the body of the essay depends on the nature of an essay. And so, we have left the writeBody() method definition for the subclasses to provide.
Let’s now create two subclasses of an EssayTemplate – a ShortEssay and a LongEssay:
public class ShortEssay extends EssayTemplate {
public ShortEssay(String topic) {
super(topic);
}
@Override
public void writeBody() {
System.out.println("Adding 2 paras");
}
}
public class LongEssay extends EssayTemplate {
public LongEssay(String topic) {
super(topic);
}
@Override
public void writeBody() {
System.out.println("Adding 6 paras");
}
}
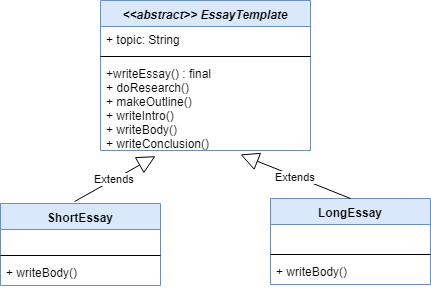
UML Diagram:
We can represent the above example implementation of a template pattern via UML diagram as:
The ShortEssay and LongEssay define their implementations of the writeBody() method. However, the method defining the algorithm along with the other common method implementations lies in the superclass.
Client Code Using Template Pattern:
Let’s write some client code to test out our implementation:
//code in main method
EssayTemplate shortEssay = new ShortEssay("Programming - An Art");
shortEssay.writeEssay();
With this, we’ll get the following output on our console:
Researching Making an outline Introducing topic Adding 2 paras Concluding topic
Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we looked at the template method pattern.
All the non-abstract methods of java.io.InputStream and java.io.OutputStream use the template pattern.